Compiling mobile applications are resource-intensive, but Coder allows you to leverage cloud resources to save time compiling while still keeping your native emulator experience.
Android
You can use the Android emulator on your local machine to build and debug apps developed remotely on Coder.
-
Install Android Studio onto your local machine.
-
Start Android Studio, and when prompted, install the SDK.
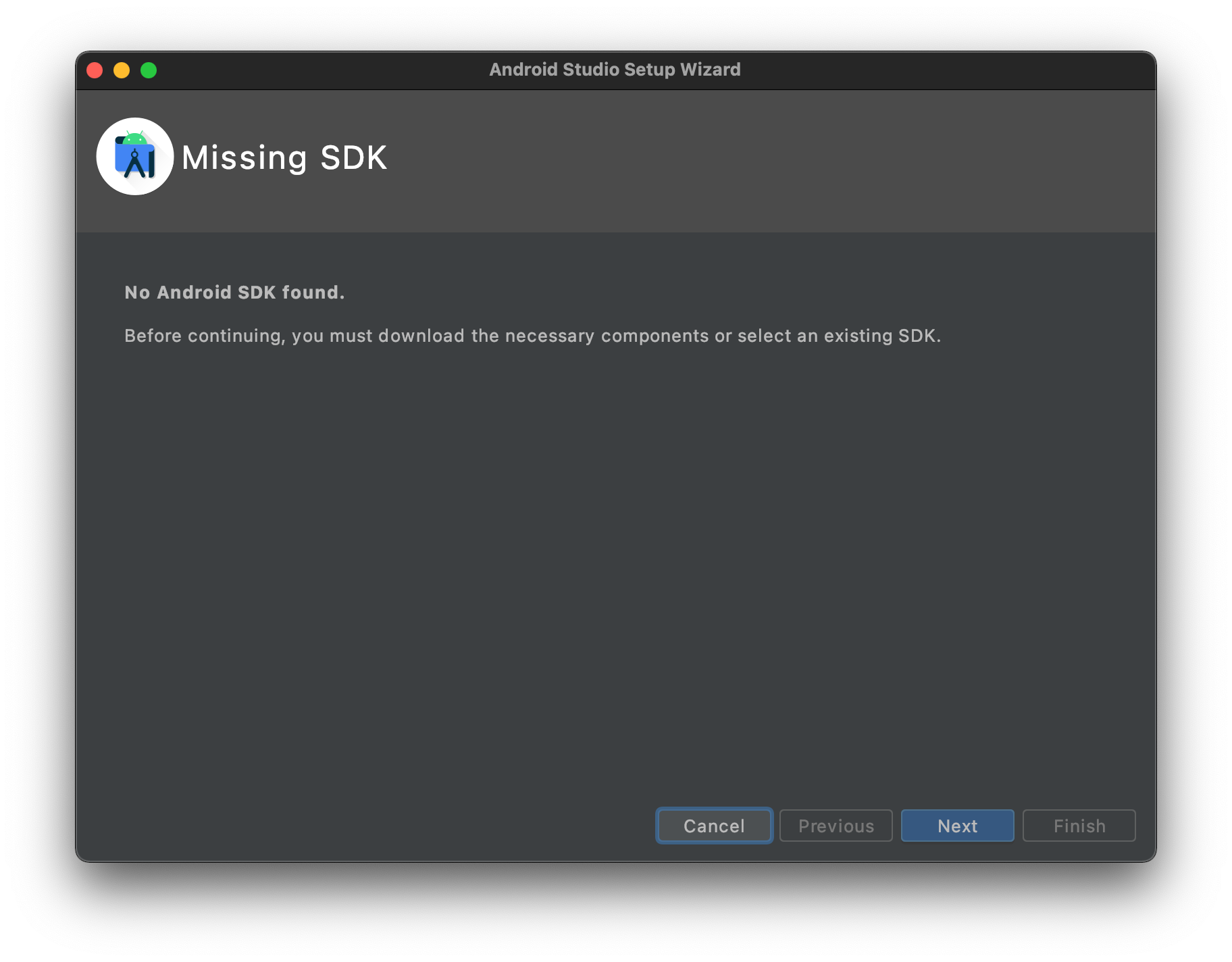
-
Create and start a Virtual Device.
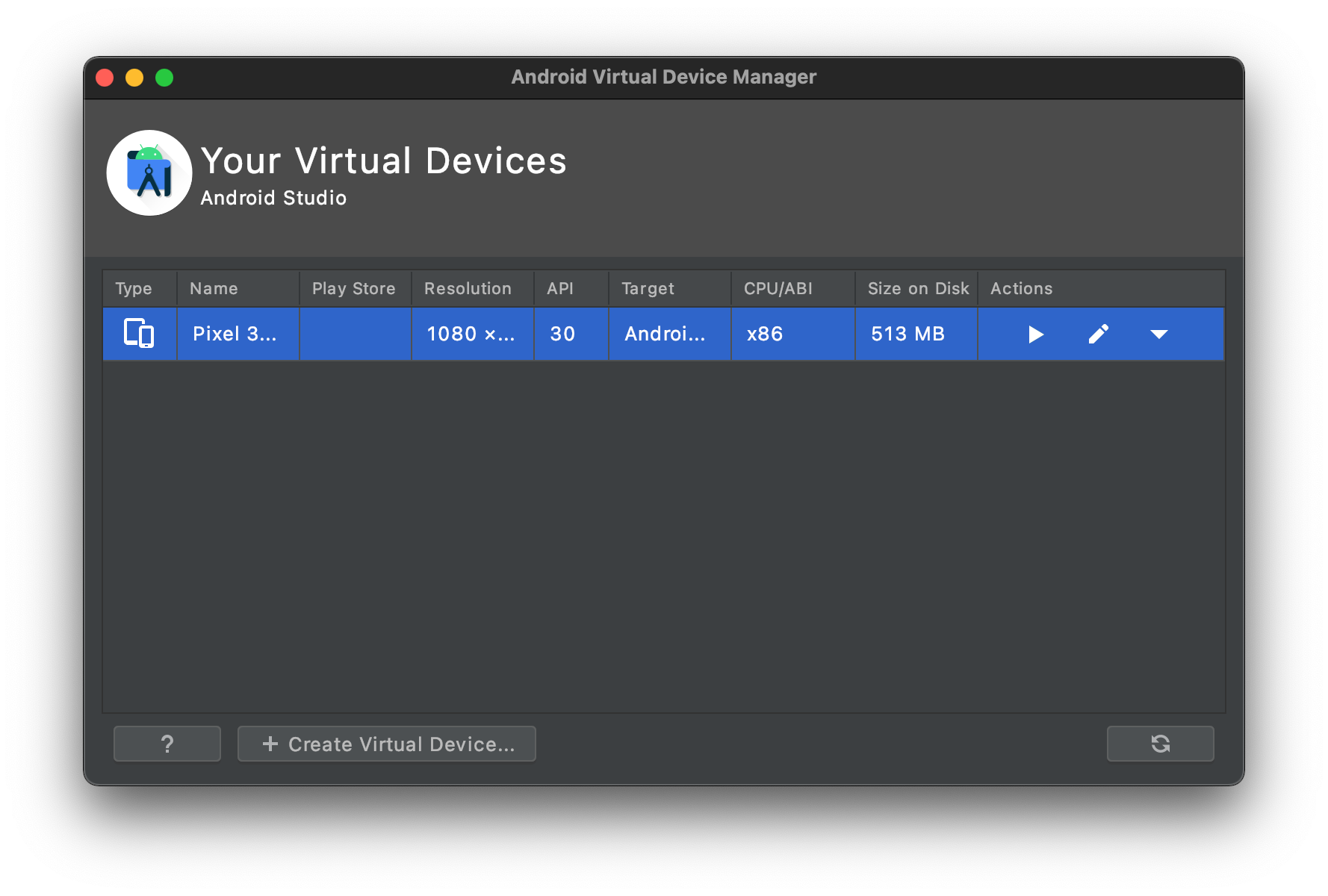
-
Create a workspace variable called
ANDROID_SDK_PATHand set it to the installation path of your Android SDK (for example, it's typically~/Library/Android/sdkon macOS andC:\Users\<USER_NAME>\AppData\Local\Android\sdkon Windows).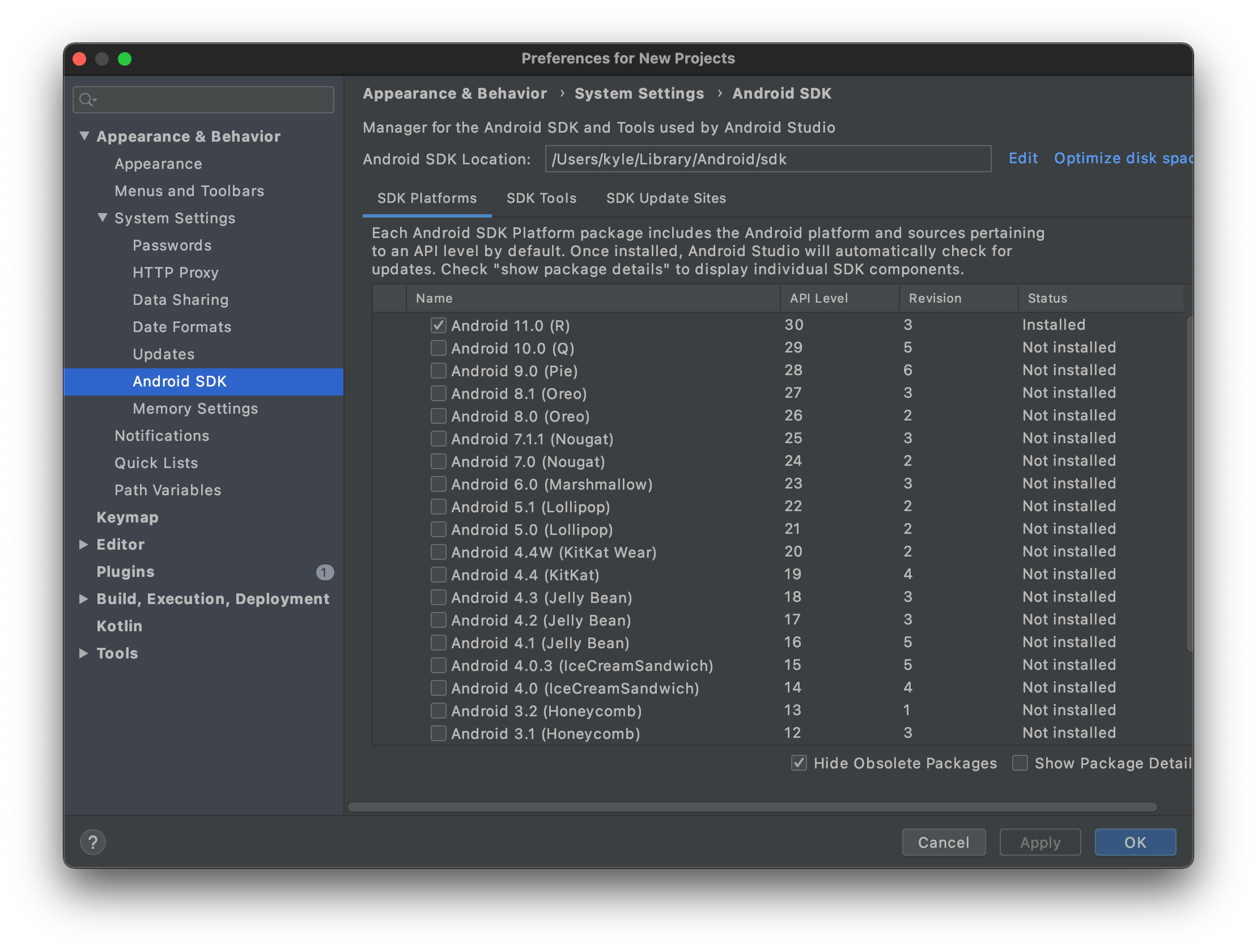
-
Start the Android Debug Server on port 5555:
$ $ANDROID_SDK_PATH/platform-tools/adb tcpip 5555 restarting in TCP mode port: 5555 -
Create a Coder workspace that includes the Android SDK; you can do this by including the following in your Dockerfile:
FROM codercom/enterprise-androidAlternatively, you can import or extend Coder's image
-
Forward your Android Debug Server to the remote workspace:
# You must have the Coder CLI installed. $ coder config-ssh $ ssh -R 5555:127.0.0.1:5555 coder.<NAME_OF_YOUR_WORKSPACE> -
Run
adb devicesto view the emulators forwarded from your local machine:$ adb devices List of devices attached emulator-5556 -
Build and run your Android applications remotely:
./gradlew android:installDebug


