Workspace Proxies
Workspace proxies provide low-latency experiences for geo-distributed teams.
Coder's networking does a best effort to make direct connections to a workspace. In situations where this is not possible, such as connections via the web terminal and web IDEs, workspace proxies are able to reduce the amount of distance the network traffic needs to travel.
A workspace proxy is a relay connection a developer can choose to use when connecting with their workspace over SSH, a workspace app, port forwarding, etc. Dashboard connections and API calls (e.g. the workspaces list) are not served over workspace proxies.
Deploy a workspace proxy
Each workspace proxy should be a unique instance. At no point should two workspace proxy instances share the same authentication token. They only require port 443 to be open and are expected to have network connectivity to the coderd dashboard. Workspace proxies do not make any database connections.
Workspace proxies can be used in the browser by navigating to the user
Account -> Workspace Proxy
Requirements
- The Coder CLI must be installed and authenticated as a user with the Owner role.
Step 1: Create the proxy
Create the workspace proxy and make sure to save the returned authentication token for said proxy. This is the token the workspace proxy will use to authenticate back to primary coderd.
$ coder wsproxy create --name=newyork --display-name="USA East" --icon="/emojis/2194.png"
Workspace Proxy "newyork" created successfully. Save this token, it will not be shown again.
Token: 2fb6500b-bb47-4783-a0db-dedde895b865:05271b4ef9432bac14c02b3c56b5a2d7f05453718a1f85ba7e772c0a096c7175
To verify it was created.
$ coder wsproxy ls
NAME URL STATUS STATUS
newyork unregistered
Step 2: Deploy the proxy
Deploying the workspace proxy will also register the proxy with coderd and make
the workspace proxy usable. If the proxy deployment is successful,
coder wsproxy ls will show an ok status code:
$ coder wsproxy ls
NAME URL STATUS STATUS
primary https://dev.coder.com ok
brazil-saopaulo https://brazil.example.com ok
europe-frankfurt https://europe.example.com ok
sydney https://sydney.example.com ok
Other Status codes:
unregistered: The workspace proxy was created, and not yet deployedunreachable: The workspace proxy was registered, but is not responding. Likely the proxy went offline.unhealthy: The workspace proxy is reachable, but has some issue that is preventing the proxy from being used.coder wsproxy lsshould show the error message.ok: The workspace proxy is healthy and working properly!
Configuration
Workspace proxy configuration overlaps with a subset of the coderd
configuration. To see the full list of configuration options:
coder wsproxy server --help
# Proxy specific configuration. These are REQUIRED
# Example: https://coderd.example.com
CODER_PRIMARY_ACCESS_URL="https://<url_of_coderd_dashboard>"
CODER_PROXY_SESSION_TOKEN="<session_token_from_proxy_create>"
# Runtime variables for "coder start".
CODER_HTTP_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0:80
CODER_TLS_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0:443
# Example: https://east.coderd.example.com
CODER_ACCESS_URL="https://<access_url_of_proxy>"
# Example: *.east.coderd.example.com
CODER_WILDCARD_ACCESS_URL="*.<app_hostname_of_proxy>"
CODER_TLS_ENABLE=true
CODER_TLS_CLIENT_AUTH=none
CODER_TLS_CERT_FILE="<cert_file_location>"
CODER_TLS_KEY_FILE="<key_file_location>"
# Additional configuration options are available.
Running on Kubernetes
Make a values-wsproxy.yaml with the workspace proxy configuration.
Notice the workspaceProxy configuration which is false by default in the
Coder Helm chart:
coder:
env:
- name: CODER_PRIMARY_ACCESS_URL
value: "https://<url_of_coderd_dashboard>"
- name: CODER_PROXY_SESSION_TOKEN
value: "<session_token_from_proxy_create>"
# Example: https://east.coderd.example.com
- name: CODER_ACCESS_URL
value: "https://<access_url_of_proxy>"
# Example: *.east.coderd.example.com
- name: CODER_WILDCARD_ACCESS_URL
value: "*.<app_hostname_of_proxy>"
tls:
secretNames:
- kubernetes-wsproxy-secret
# enable workspace proxy
workspaceProxy: true
Using Helm, install the workspace proxy chart
helm install coder coder-v2/coder --namespace <your workspace proxy namespace> -f ./values-wsproxy.yaml
Test that the workspace proxy is reachable with curl -vvv. If for some reason,
the Coder dashboard still shows the workspace proxy is UNHEALTHY, scale down
and up the deployment's replicas.
Running on a VM
# Set configuration options via environment variables, a config file, or cmd flags
coder wsproxy server
Running as a system service
If you've installed Coder via a system package, you
can configure the workspace proxy by settings in
/etc/coder.d/coder-workspace-proxy.env
To run workspace proxy as a system service on the host:
# Use systemd to start workspace proxy now and on reboot
sudo systemctl enable --now coder-workspace-proxy
# View the logs to ensure a successful start
journalctl -u coder-workspace-proxy.service -b
To restart workspace proxy after applying system changes:
sudo systemctl restart coder-workspace-proxy
Running in Docker
Modify the default entrypoint to run a workspace proxy server instead of a regular Coder server.
Docker Compose
Change the provided
compose.yml
file to include a custom entrypoint:
image: ghcr.io/coder/coder:${CODER_VERSION:-latest}
+ entrypoint: /opt/coder wsproxy server
Docker run
docker run --rm -it --entrypoint /opt/coder ghcr.io/coder/coder:latest wsproxy server
Custom Dockerfile
FROM ghcr.io/coder/coder:latest
ENTRYPOINT ["/opt/coder", "wsproxy", "server"]
Selecting a proxy
Users can select a workspace proxy at the top-right of the browser-based Coder dashboard. Workspace proxy preferences are cached by the web browser. If a proxy goes offline, the session will fall back to the primary proxy. This could take up to 60 seconds.
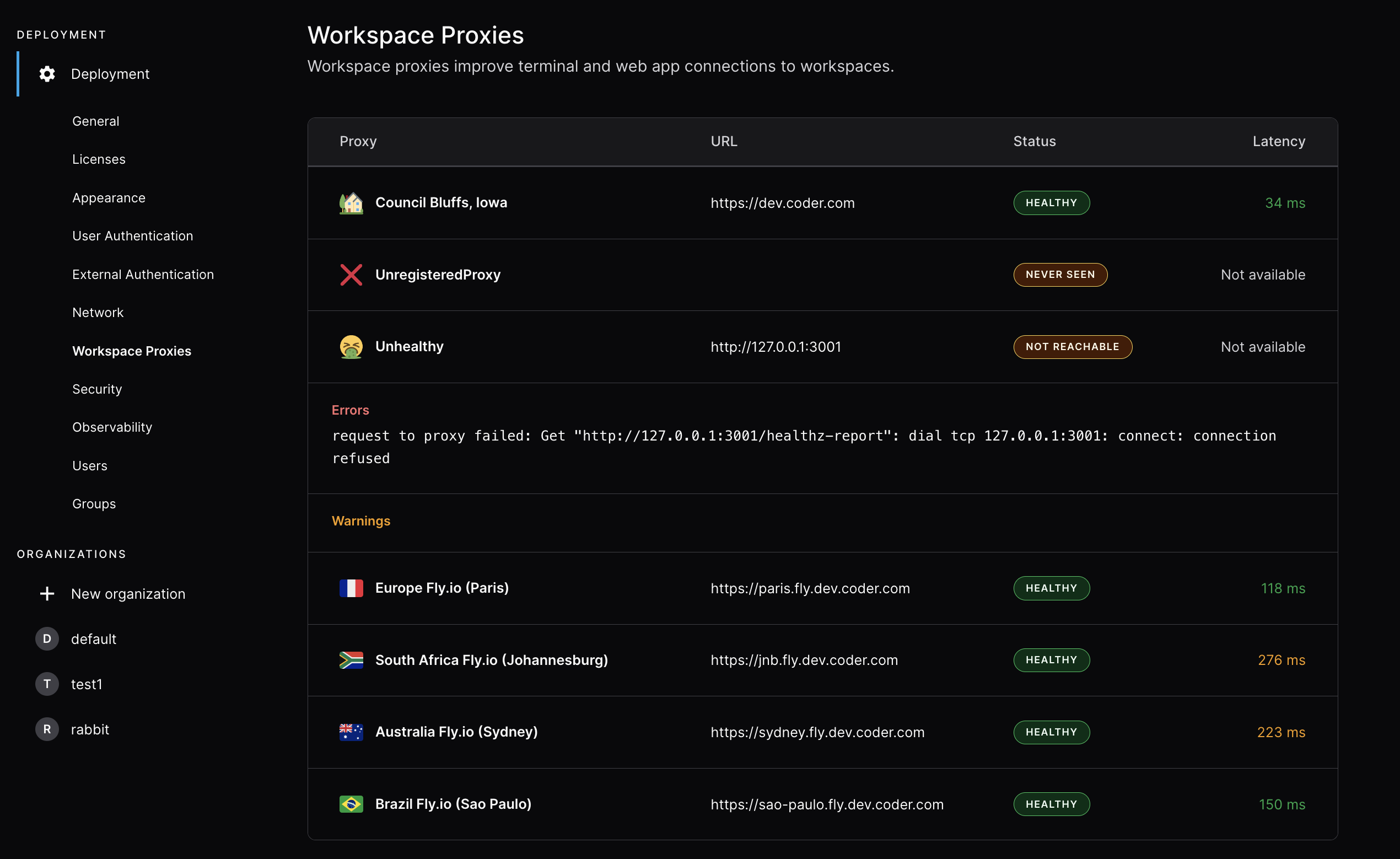
Multiple workspace proxies
When multiple workspace proxies are deployed:
- The browser measures latency to each available proxy independently.
- Users can select their preferred proxy from the dashboard.
- The system can automatically select the lowest-latency proxy.
- The dashboard latency indicator shows latency to the currently selected proxy.
Observability
Coder workspace proxy exports metrics via the HTTP endpoint, which can be
enabled using either the environment variable CODER_PROMETHEUS_ENABLE or the
flag --prometheus-enable.
The Prometheus endpoint address is http://localhost:2112/ by default. You can
use either the environment variable CODER_PROMETHEUS_ADDRESS or the flag
--prometheus-address <network-interface>:<port> to select a different listen
address.


