1. Import an image
Ensure you've imported an image for your workspace to use.
2. Create a workspace
If this is your first time using Coder, you'll see a Create Workspace button in the middle of your screen; otherwise, you'll see a list of your existing workspaces. Click the New Environment button and choose Custom Workspace.
To learn more about creating an environment from templates, see Workspaces as code.
-
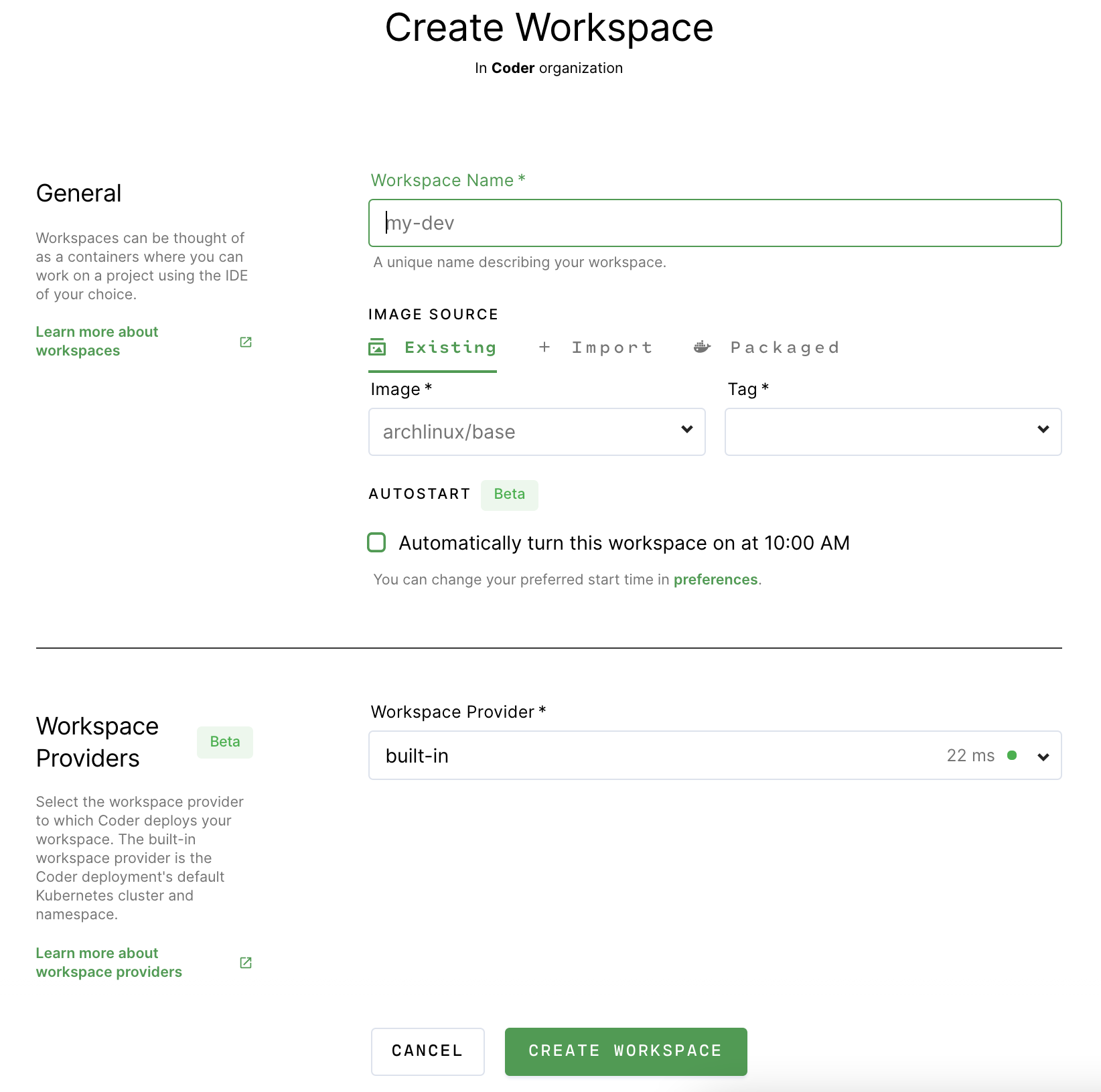
Enter a friendly name for your workspace, and choose an image to use.
-
Set the parameters for your workspace.
-
Click Create to proceed.
Coder redirects you to an overview page for your workspace during the build process. Learn more about the workspace creation parameters.
Your workspace persists in the home directory, updates to new versions of the image, and runs custom configuration on startup. Learn about the workspace lifecycle.
Advanced
Coder provides advanced settings that allow you to customize your workspace.
If your Coder deployment has container-based virtual machines enabled, Coder creates your workspace as a CVMs by default (you can opt-out of this setting by unchecking the Run as Container-based Virtual Machine box).
You can also specify the resources Coder should allocate.
By default, Coder allocates resources (CPU Cores, Memory, and Disk Space) based on the parent image.
Coder displays a warning if you choose your resource settings and they're less than the image-recommended default, but you can still create the workspace.
3. Start Coding
Once you've created a workspace, it's time to hop in. Read more about how to connect your favorite editor or IDE with your new workspace!
Integrate with Git to have your SSH key injected automatically into Workspaces.


