This article will walk you through the process of getting started with a Coder workspace capable of supporting data science projects. You'll learn how to:
- Connect Coder to your Git provider (this example assumes that you're using GitHub, but Coder supports GitLab and Bitbucket as well));
- Create a workspace with Jupyter Notebook and other data science packages present;
- Add a sample project to your workspace, specifically one as a Jupyter Notebook using IMDB movie data.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes that you have a Coder deployment available to you and that you have the credentials needed to access the deployment.
Step 1: Log in and connect Coder to your Git provider
In this step, you'll log into Coder, then link your Coder account with your Git provider. This will allow you to do things like pull repositories and push changes.
-
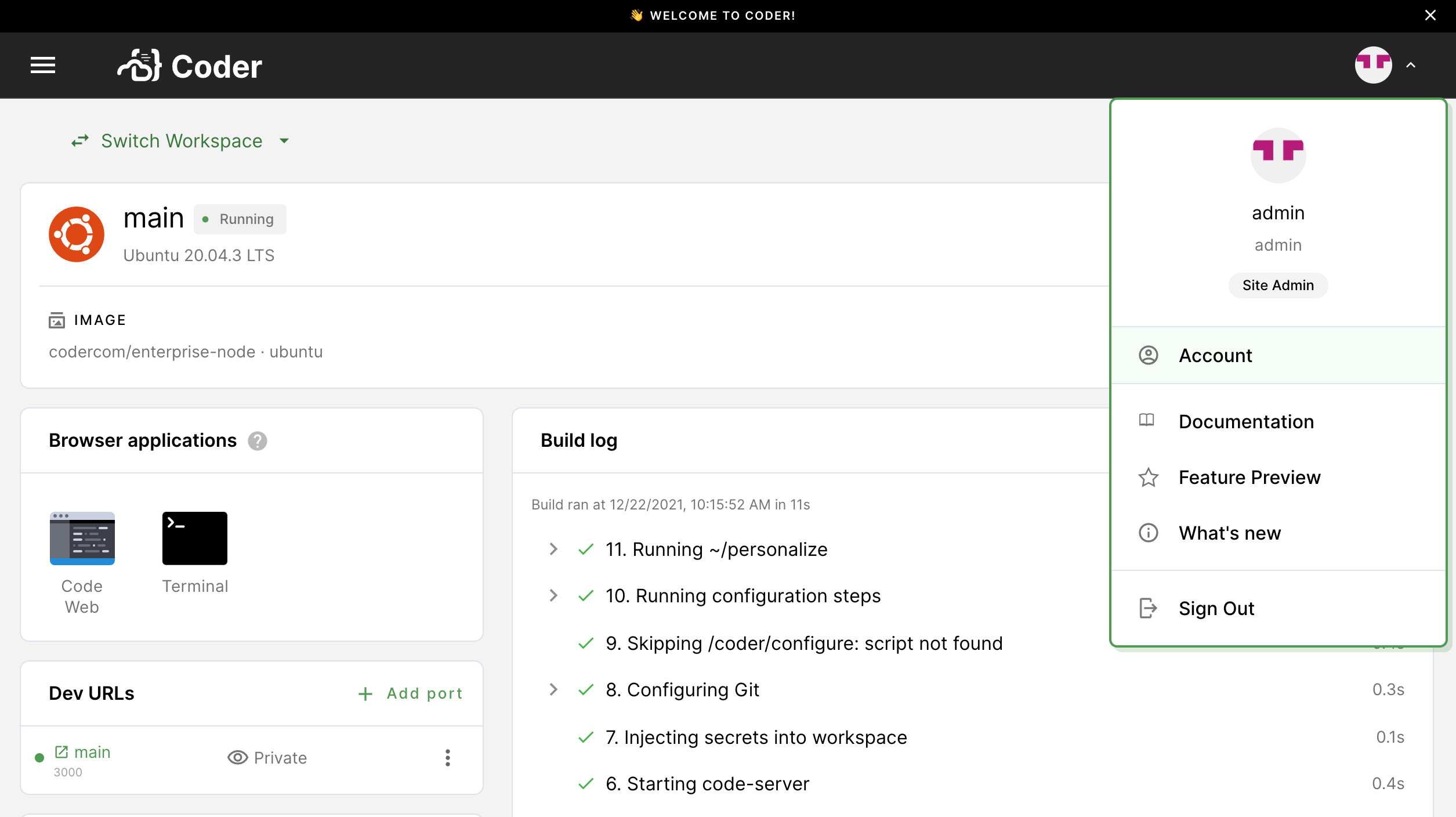
Navigate to the Coder deployment using the URL provided to you by your site manager, and log in.
-
Click on your avatar in the top-right, and select Account.
-
Provide Coder with your SSH key to connect and authenticate to GitHub.
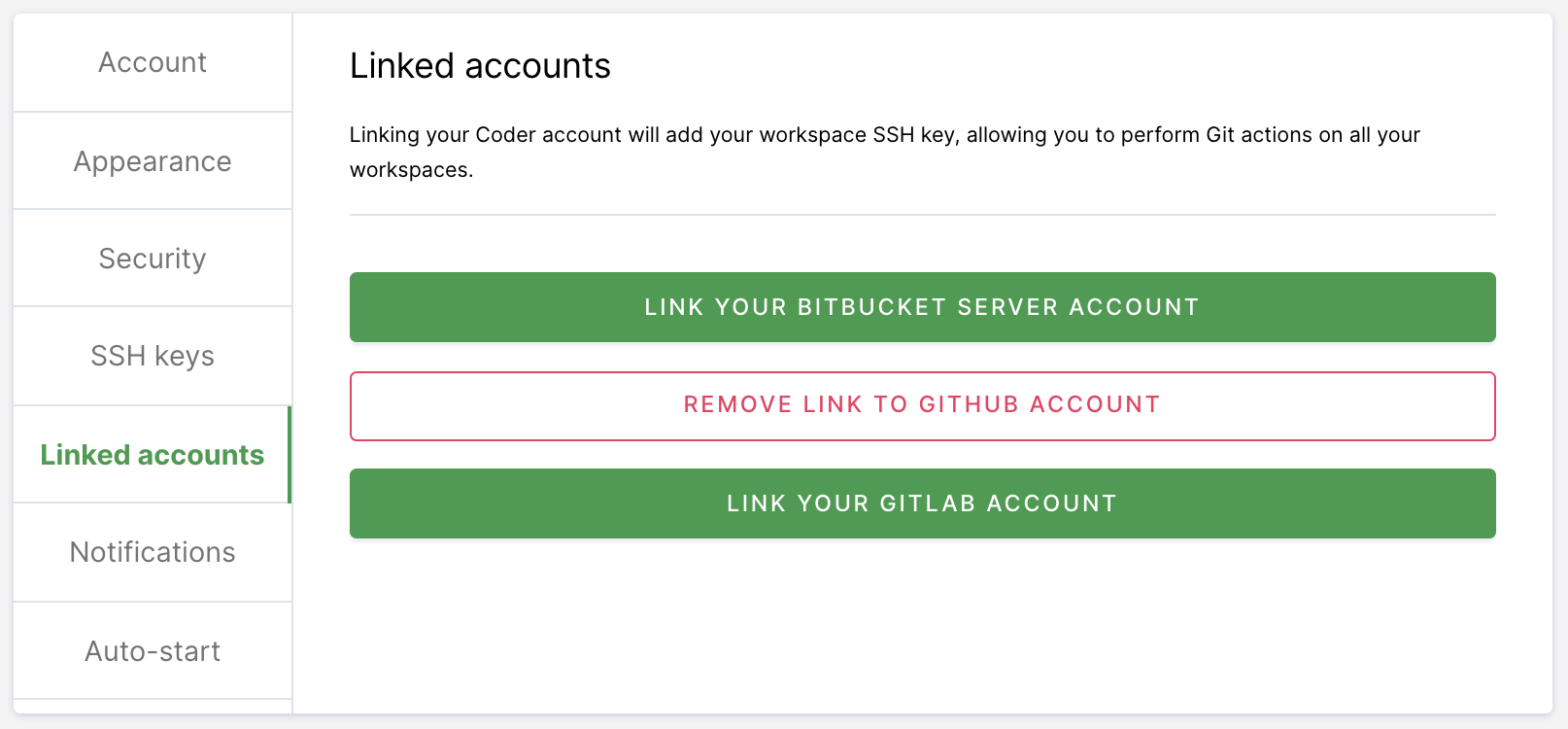
If your site manager has configured OAuth, go to Linked Accounts and follow the on-screen instructions to link your GitHub account.
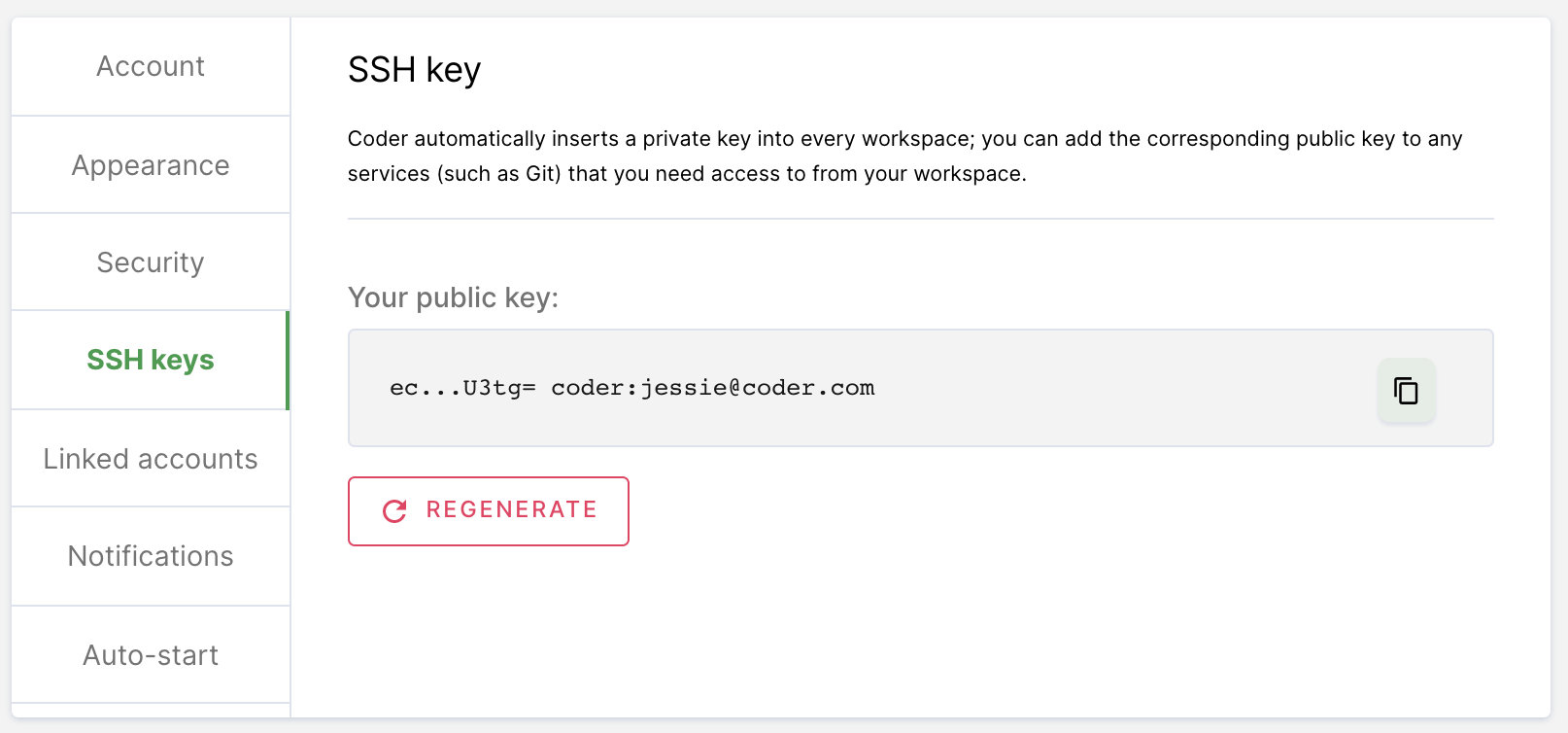
If your site manager has not configured OAuth or you are using a Git provider that Coder does not support, go to SSH keys. Copy your public SSH key and provide it to GitHub.
Step 2: Import an image
At this point, you'll import your image, which you can think of as a template
for your workspace. This template contains the language version, tooling, and
dependencies you need to work on the project. In this case, the image also
contains a configure script that will clone the data science project from
GitHub to your workspace.
To import an image:
-
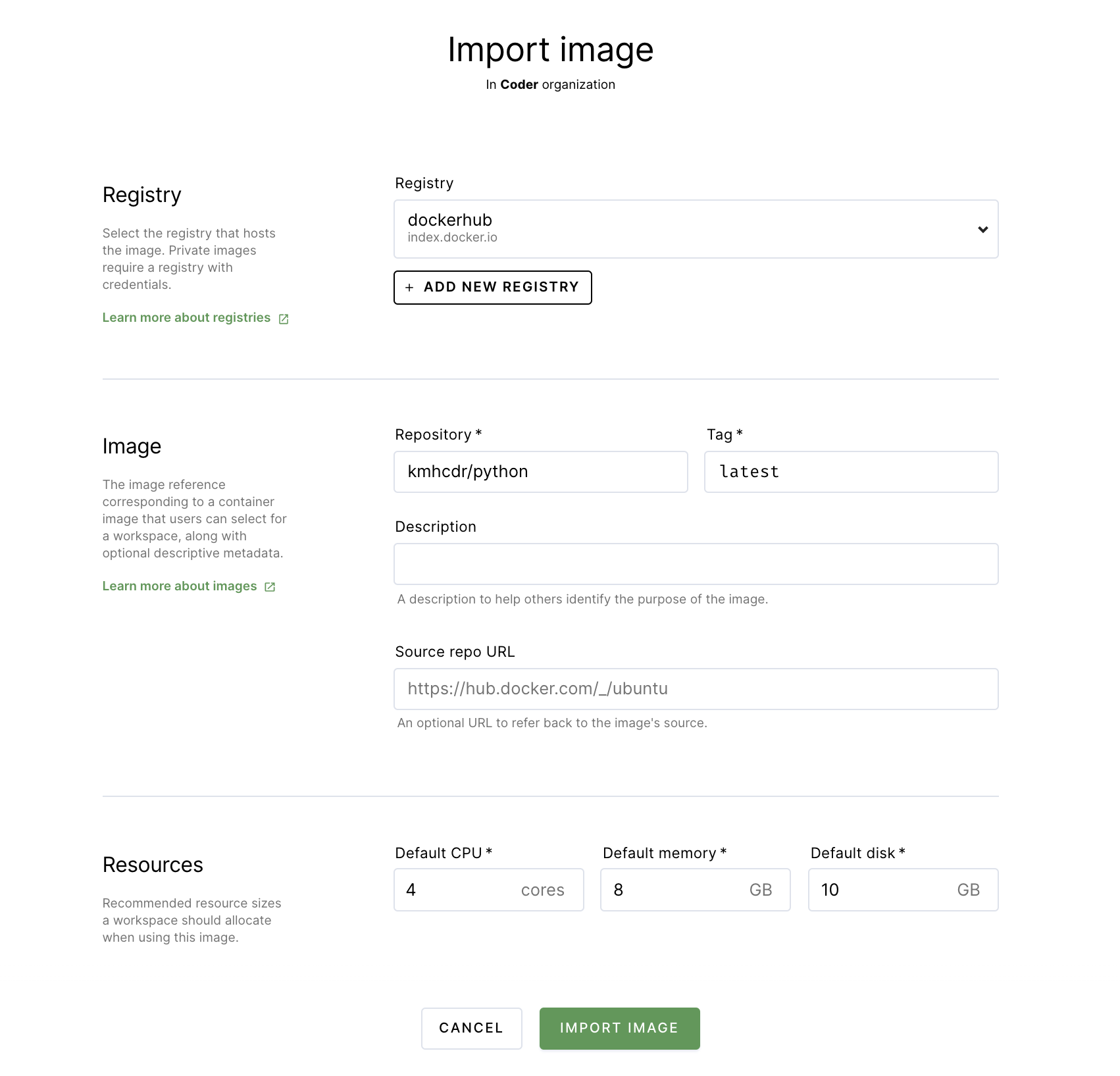
In the top navigation bar, click Images. Then, click on Import Image.
-
Leave the default registry (which is dockerhub) selected.
-
Under repository, provide kmhcdr/python. Provide latest as the tag. Optionally, you can provide a description of the image
-
Specify the minimum amount of resources (cores, memory, and disk space) the workspace should have when using this image. For this project, we recommend 4 cores, 8 GB memory, and 10 GB disk space as a starting point.
-
Click Import Image.
Step 3: Create your workspace
You will now create the workspace where you'll work on your development project.
-
Return to Workspaces using the top navigation bar.
-
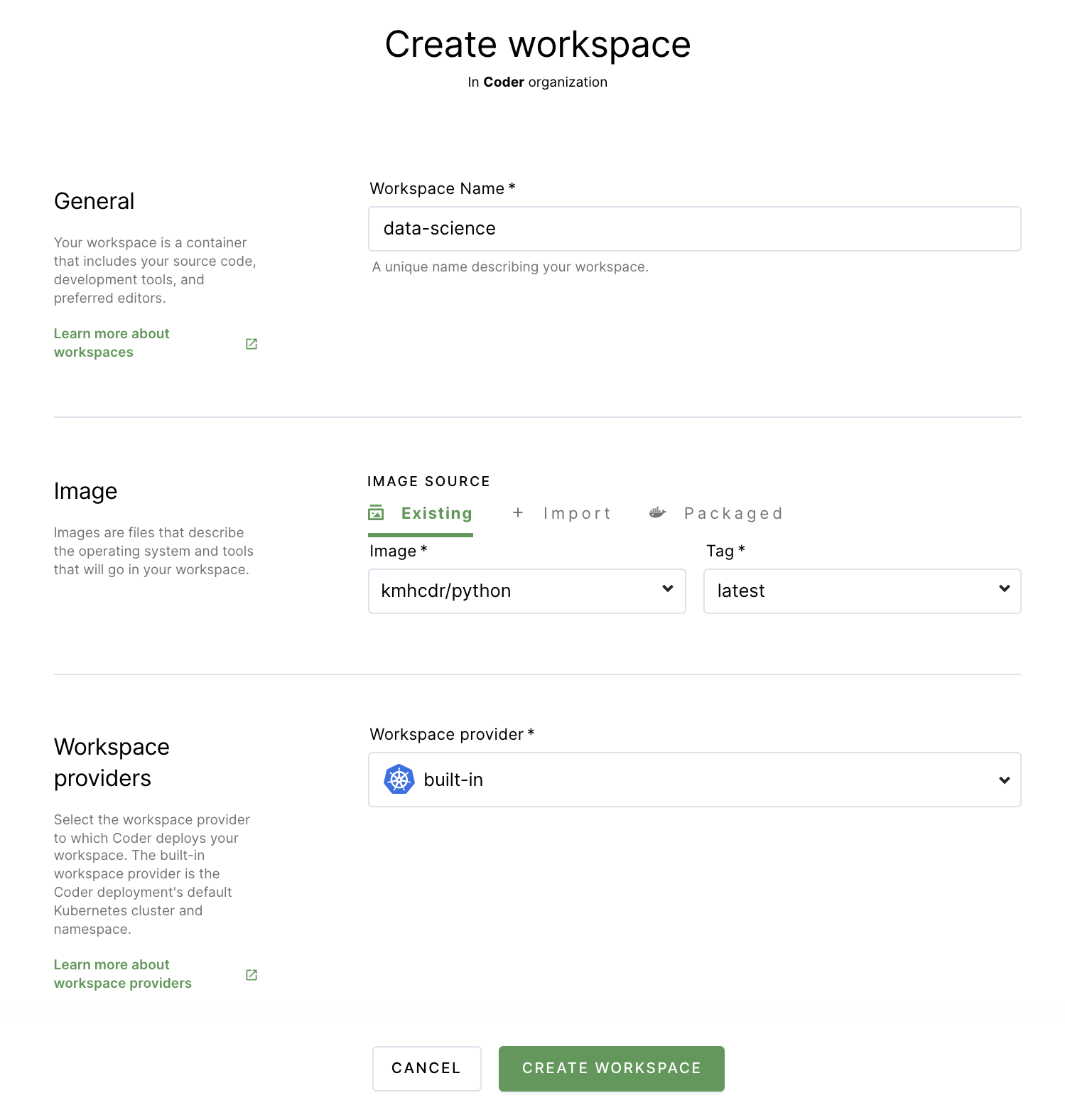
Click New workspace to launch the workspace-creation dialog.
-
Provide a Workspace Name.
-
In the Image section, select the kmhcdr/python image you just imported.
-
Under Workspace providers, leave the default option (which is built-in) selected.
-
Expand the Advanced section. If the Run as a container-based virtual machine option is selected, unselect the box. Leave the CPU, Memory, Disk, and GPU allocations as-is.
-
Scroll to the bottom, and click Create workspace. The dialog will close, allowing you to see the main workspace page. You can track the workspace build process using the Build log on the right-hand side.
Due to the number of packages present in the image, this might take few minutes.
Once your workspace is ready for use, you'll see a chip that says Running next to the name of your workspace.
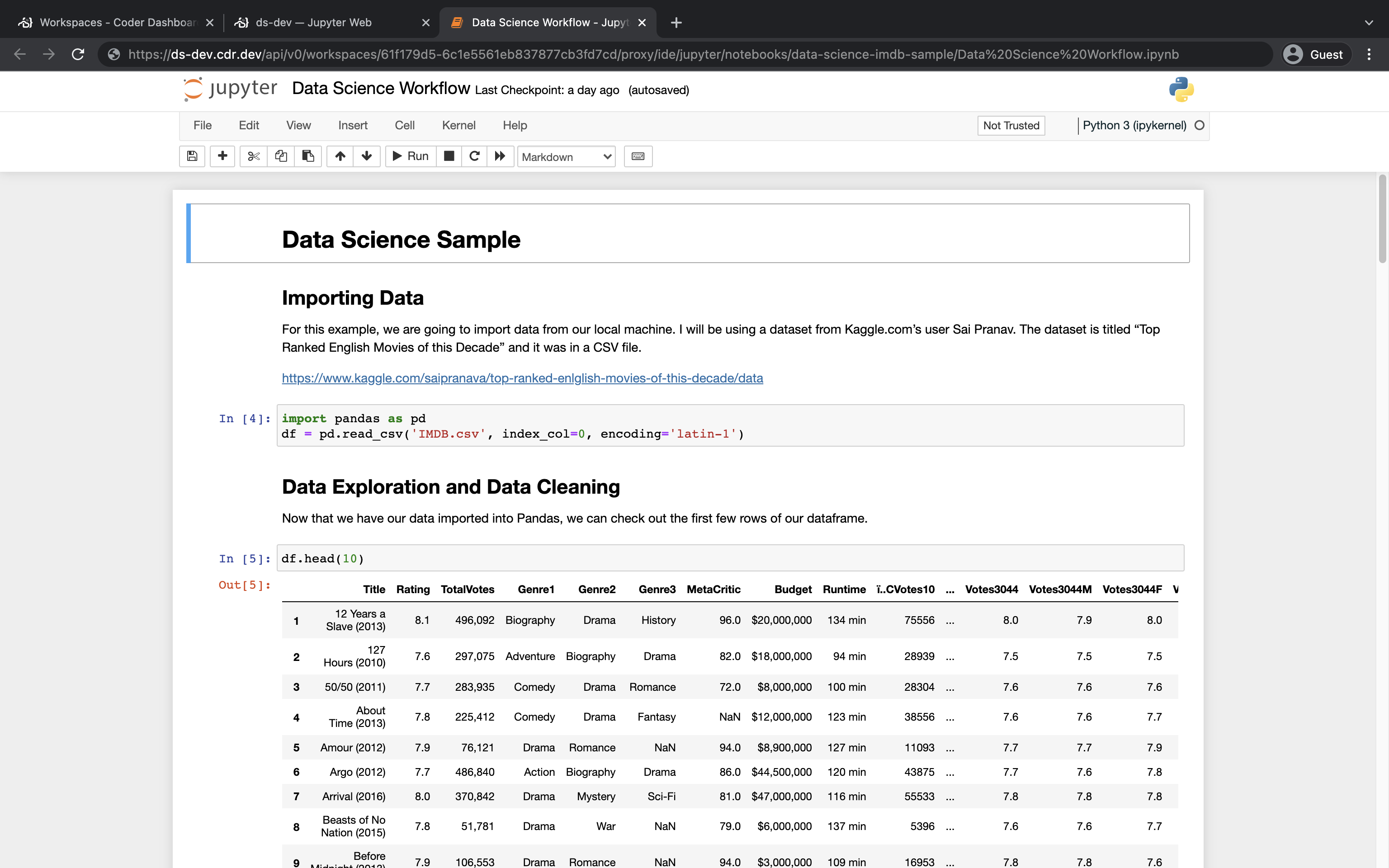
Step 4: Open up the sample project
At this point, you're ready to open up Jupyter to access your notebook.
-
Under Browser applications, click Jupyter to open the IDE in a new browser tab.
-
Under Files, click to open the data-science-imdb-sample project.
-
Click Data Science Workflow.ipynb to launch the notebook.
You're now ready to proceed with work on the project.