AI Bridge
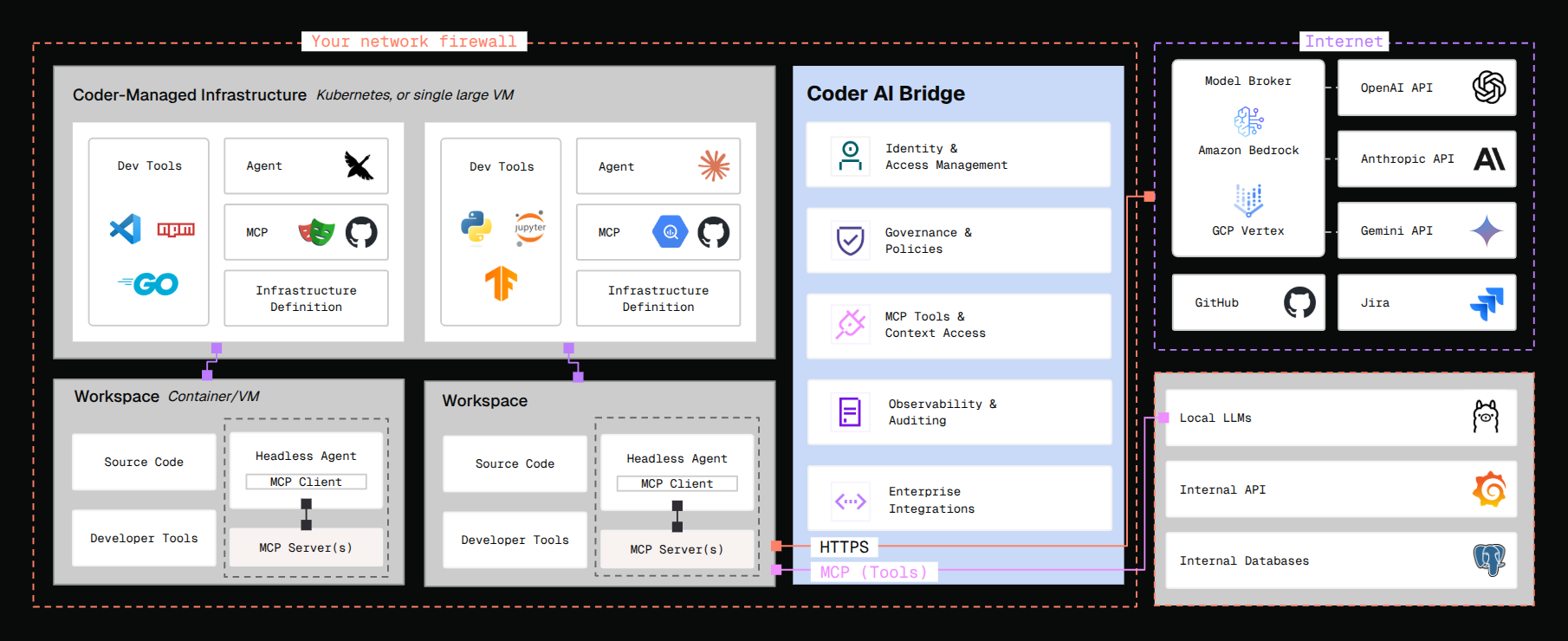
AI Bridge is a smart gateway for AI. It acts as an intermediary between your users' coding agents / IDEs and providers like OpenAI and Anthropic. By intercepting all the AI traffic between these clients and the upstream APIs, AI Bridge can record user prompts, token usage, and tool invocations.
AI Bridge solves 3 key problems:
- Centralized authn/z management: no more issuing & managing API tokens for OpenAI/Anthropic usage.
Users use their Coder session or API tokens to authenticate with
coderd(Coder control plane), andcoderdsecurely communicates with the upstream APIs on their behalf. - Auditing and attribution: all interactions with AI services, whether autonomous or human-initiated, will be audited and attributed back to a user.
- Centralized MCP administration: define a set of approved MCP servers and tools which your users may use.
When to use AI Bridge
As LLM adoption grows, administrators need centralized auditing, monitoring, and token management. AI Bridge enables organizations to manage AI tooling access for thousands of engineers from a single control plane.
If you are an administrator or devops leader looking to:
- Measure AI tooling adoption across teams or projects
- Establish an audit trail of prompts, issues, and tools invoked
- Manage token spend in a central dashboard
- Investigate opportunities for AI automation
- Uncover high-leverage use cases last
AI Bridge is best suited for organizations facing these centralized management and observability challenges.


