If you have configuration instructions that apply to everyone who uses a given image to create workspaces, you can define them using the /coder/configure file.
You can use the configure script to:
- Run Coder CLI commands
- Check for and clone a GitHub repo if it isn't present
- Run scripts using CODER_* environment variables
Coder will check the image for the presence of a /coder/configure file during the build process; if Coder finds one, it will execute the instructions contained.
The following steps will show you how to create and use a config file.
Step 1: Create the configure file
Using the text editor of your choice, create a file named configure and make
it executable:
touch configure
chmod +x configure
Next, add the instructions that you want included. For example, the following file shows how you can clone a repo at build time:
#!/bin/bash
if [ ! -d "/home/coder/workspace/project" ]
then
git clone git://company.com/project.git /home/coder/workspace/project
else
echo "Project has already been cloned."
fi
Note that the instructions provided include logic on whether the instructions should be re-run (and when) or if Coder should run the instructions only once. We strongly recommend including this logic at all times to minimize overhead.
Step 2: Add the config file to the image
Once you have a config file, update your image to use it by including the following in your Dockerfile:
COPY [ "configure", "/coder/configure" ]
As an example, take a look at the sample Docker file that follows; the final line includes instructions to Coder on copying the settings from the configure file:
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl
COPY [ "configure", "/coder/configure" ]
Step 3: Build and push the image and config file
To make your image accessible to Coder, build the development image and push it to the Docker registry.
To build your image, run the following command in the directory where your Dockerfile is located (be sure to replace the cdr/config placeholder value with your tag and repository name so that the image is pushed to the appropriate location):
docker build cdr/config .
Once you've built the image, push the image to the Docker registry:
docker push cdr/config
Step 4: Test the config file
You can test your setup by performing the following steps:
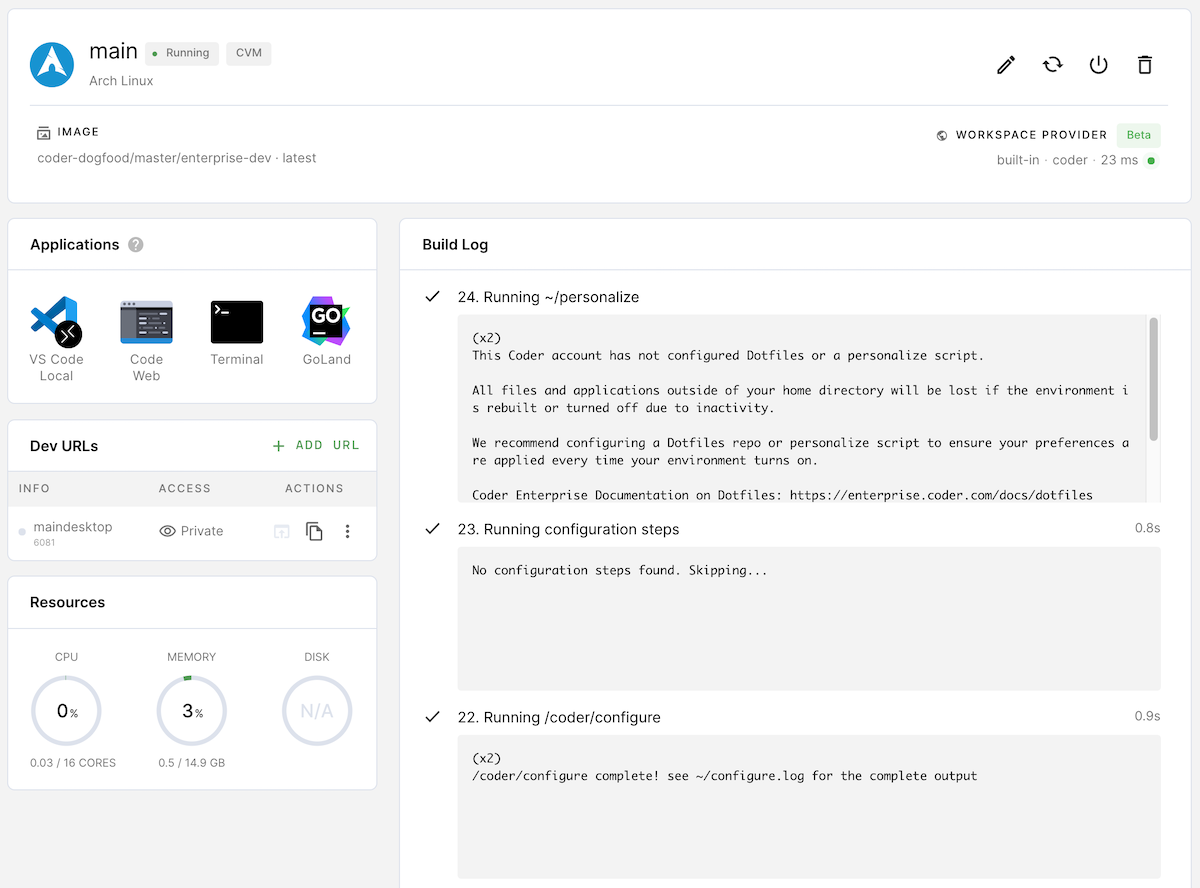
Coder will run the configure file during the build process, and you can verify this using the Workspace Overview page (Coder runs the configure file as the penultimate step of the build process):
Examples
The following are examples of instructions you can include in your configure file.
Copying Coder's sample config file
Coder's base images include a basic configure script, which you can copy and modify:
# Dockerfile
FROM ...
COPY configure /coder/configure
Extending a configure script in a base image
If you're extending a Coder image that has a configure file that you'd like to preserve, the following steps show you how to avoid writing over the original script.
-
Create the configure script
touch configure chmod +x configure -
Modify the image's Dockerfile to move the original configure script (this results in Coder using the configure script that you created in the previous step while preserving the original script)
# Dockerfile FROM codercom/enterprise-configure:ubuntu USER root RUN mv /coder/configure /coder/configure-first # Add the new configure script COPY configure /coder/configure -
Create your new script; in addition to any instructions that you add, this script will run the configure script that came with the base image
# Configure # Run the initial configure script sh /coder/configure-first print "And some more commands..." ...
Running Coder CLI commands
The following shows how to run a Coder CLI command in your configure script by demonstrating how you can create a Dev URL:
# configure
coder ...
# Create a Dev URL (or update if it already exists)
coder urls create $CODER_WORKSPACE_NAME 3000 --name webapp
Modifying VS Code settings
-
Create a
settings.jsonfile:touch settings.json chmod +x settings.json -
Add settings info to your file:
{ "git.enableSmartCommit": true, "git.confirmSync": false, "editor.formatOnSave": true } -
Update
configureto use the settings file:# configure # Check if there are existing settings if [ -f "/home/coder/.local/share/code-server/User/settings.json" ] then echo "VS Code settings are already present. Remove with and run /coder/configure to revert to defaults" else cp settings.json /home/coder/.local/share/code-server/User/settings.json # Install extensions /var/tmp/coder/code-server/bin/code-server --install-extension esbenp.prettier-vscode fi


